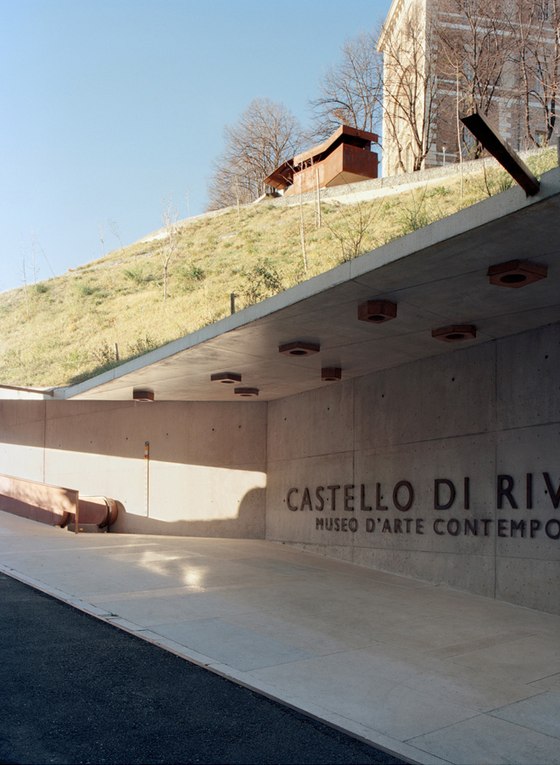
The aim of the new circulation system at the Castello di Rivoli and the redesign of the southeast flank of the adjoining hillside is to create a closer link between the city and the castle. Rivoli, a small town on the western edge of Turin, is dominated by this monumental eighteenth-century Juvarra building, which was never completed. The castle, the culmination of a 13-kilometer-long baroque axis heading from the city to the countryside, sits atop a moraine. Castello di Rivoli currently houses an internationally renowned museum of contemporary art. The hill’s ridge is one of the city’s most important green spaces, while the largely unused areas surrounding the castle – particularly those on the southeast – hold potential for urban recreational space of the first order. The design seeks to use the outdoor spaces sustainably and link them more closely to the museum.
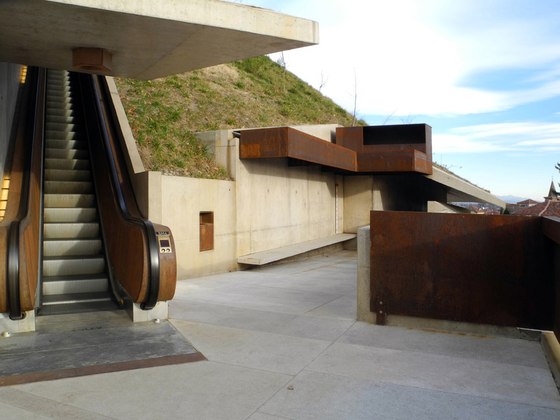
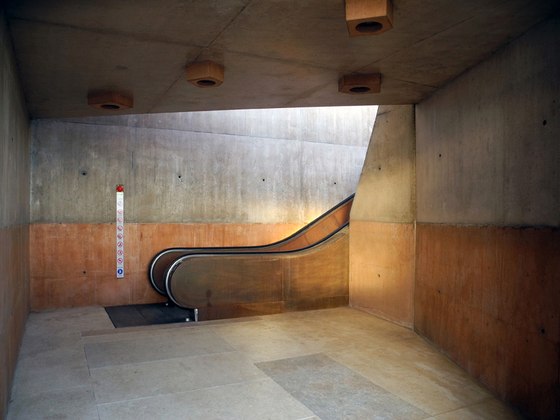
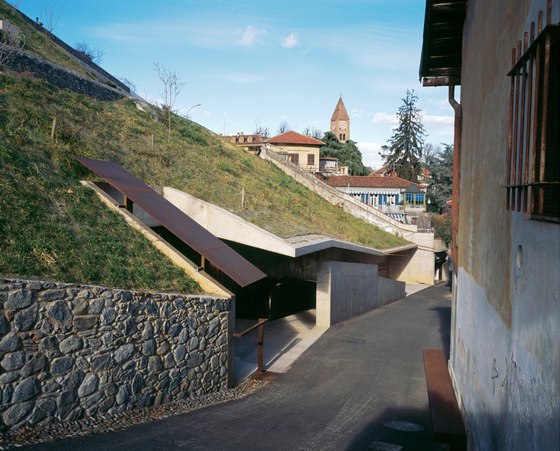
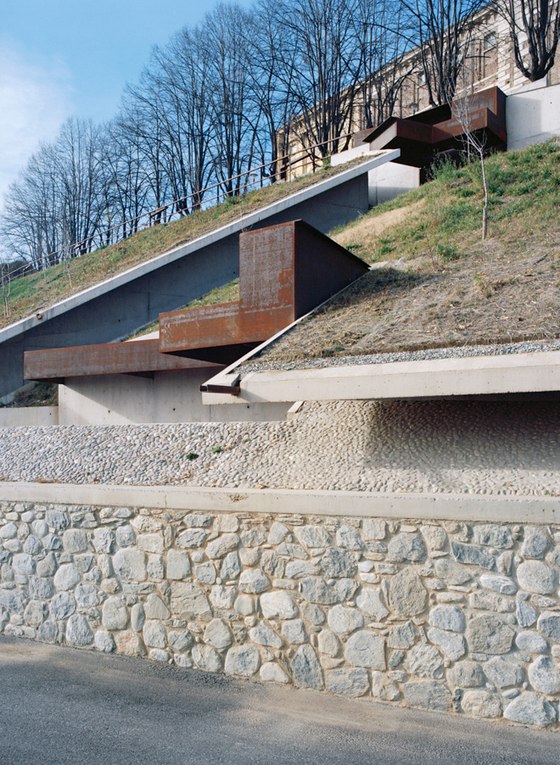
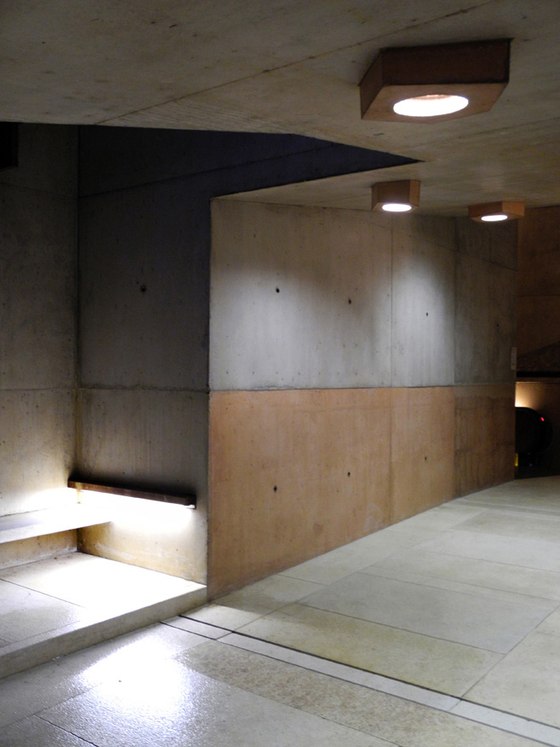
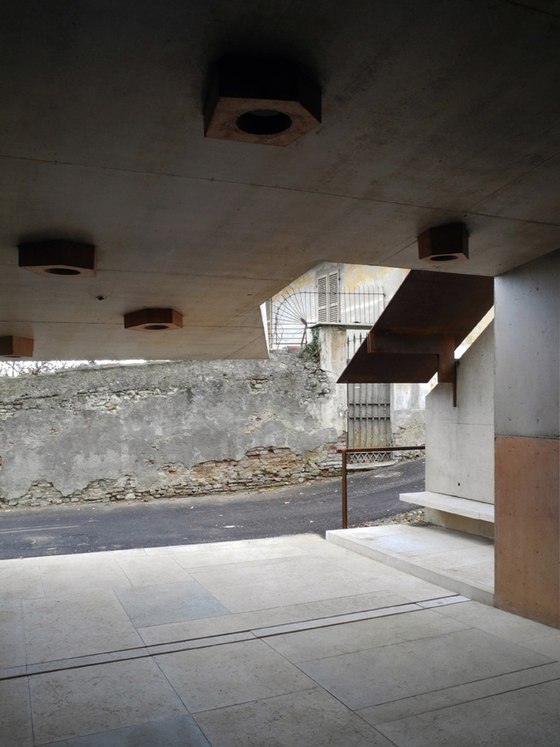
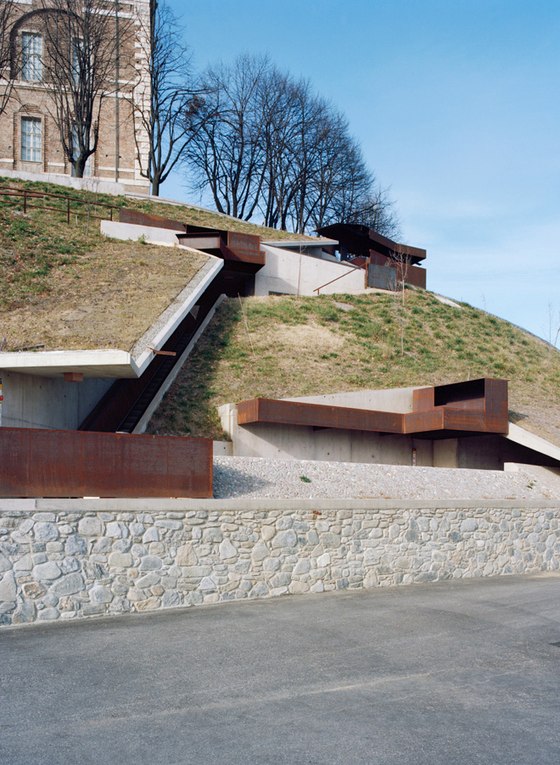
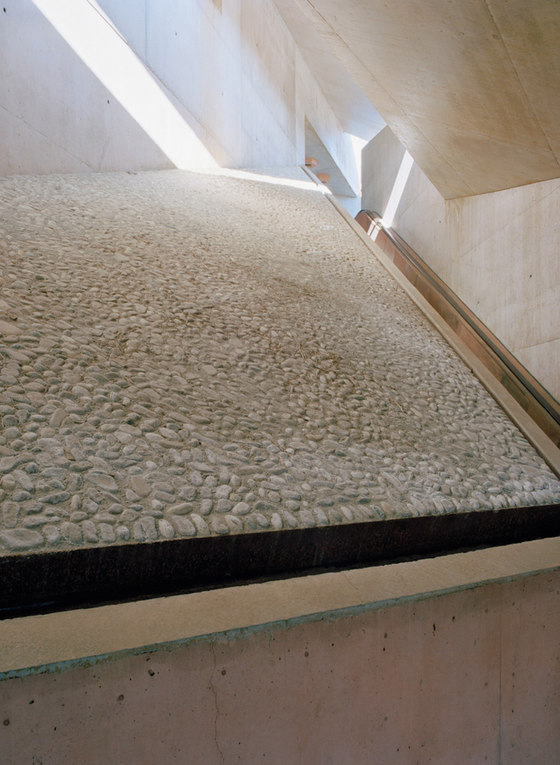
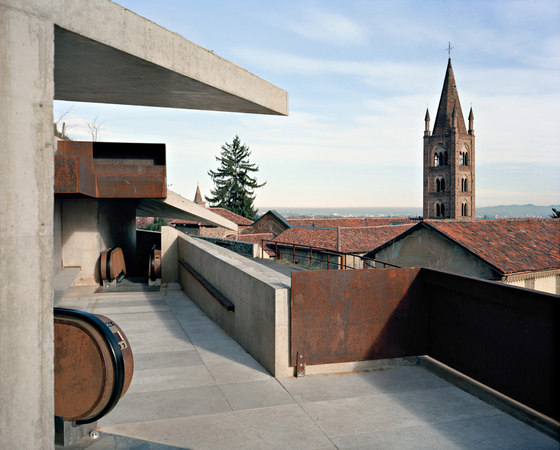
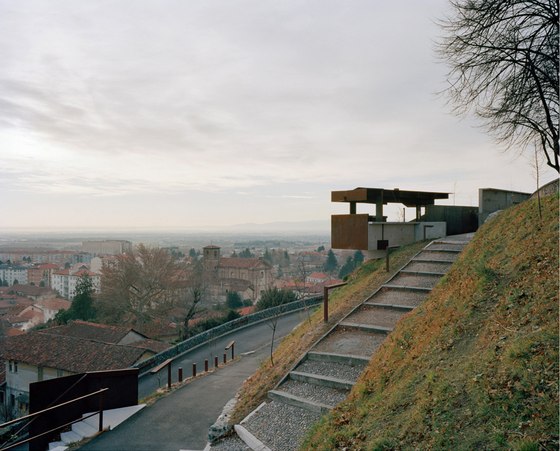
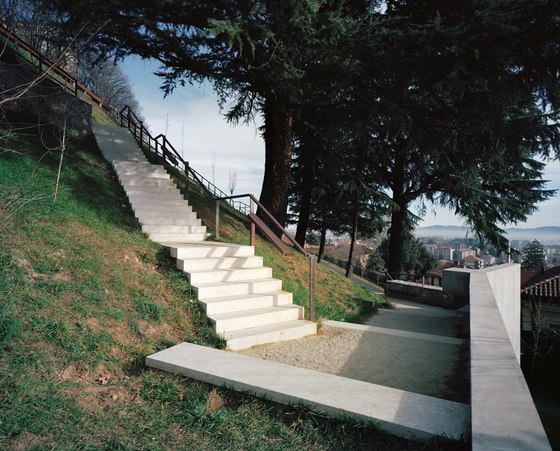
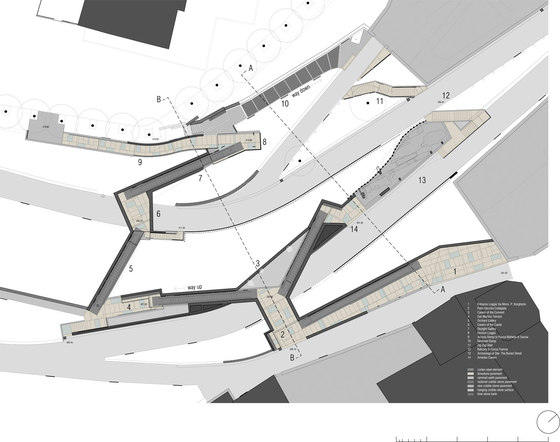
The prominent southeast slope of the hill, the site of the intervention, takes on a new key role. Across from the historic approach to the castle on the northwest side of the hill, facing away from the city, due to its location between the city’s “back” side and the incomplete garden wing of the castle (its monumental terraces were never realized), it remained inaccessible and undefined, an “inner periphery” – for centuries. The divergent scales of the city and the castle come together unmitigated in this interstitial space. This tension creates the setting for sustainable, not-for-profit uses, and can thus be manifest in a positive manner. The design lodges this inner periphery in the consciousness of the city’s residents and visitors on three different levels: as urban landscape with a new planting concept, as recreational space within walking distance, and, by means of the escalators and ramps incised in the hillside, as a direct connection. The small-scale building components in coloured concrete and Corten steel, as well as the surfaces wrought in Istrian limestone, gravel, and rammed earth emerge from the otherwise completely green hillside.
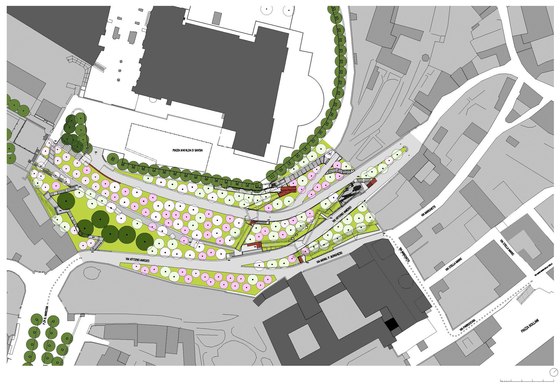
-Planting concept: By introducing plum, almond and mirabelle trees, the entire hillside is redefined as a third entity, an orchard situated between the city and the castle and making reference to the decaying fruit-growing at the foot of the Alpine crescent, whose location gave rise to the region’s name (Piemont = foot of the mountain), and which were the basis of the historic kingdom’s economy. At the same time, they constitute a counterweight to the intended display of power of the unrealized baroque gardens.
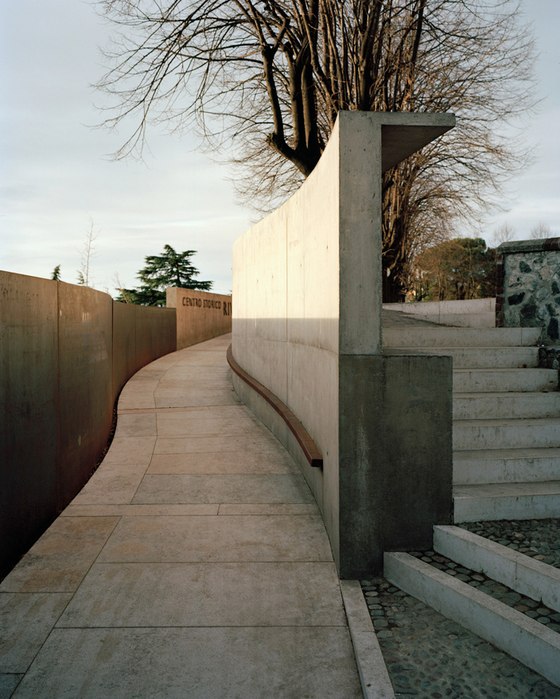
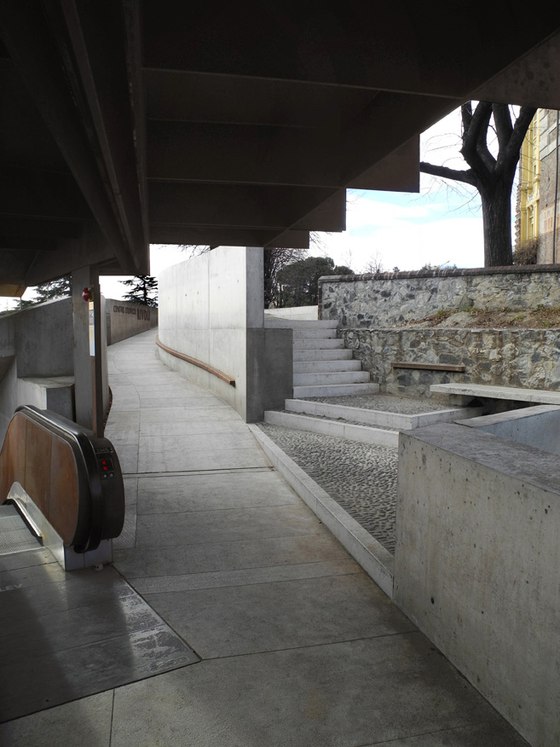
-Paths and stopping points: The existing narrow streets, which served more to reroute traffic around the city centre than to provide access to the castle, have now been closed to automobile traffic and are the framework for the new system of paths. Embedded in the orchard, a truncated piece of an old street tied into the overall design via stairs and ramps serves as a place to pass time. A group of mature cedars shades a new system of stairs that is interspersed with terraces and flat segments of the path.
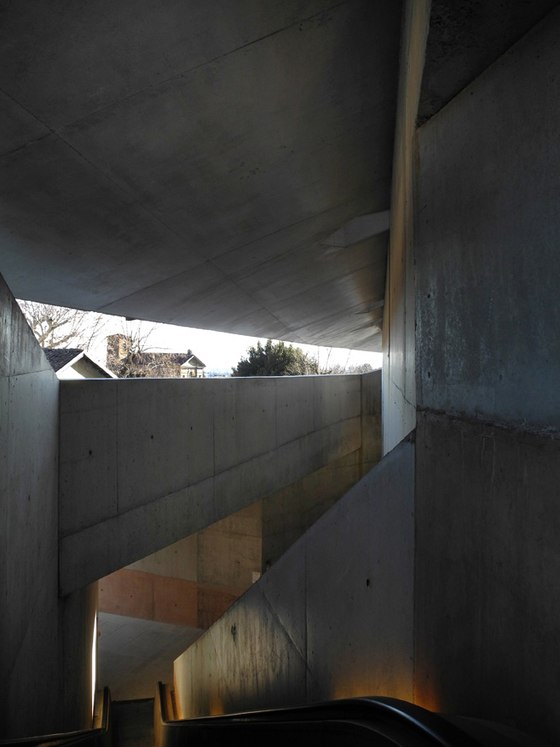
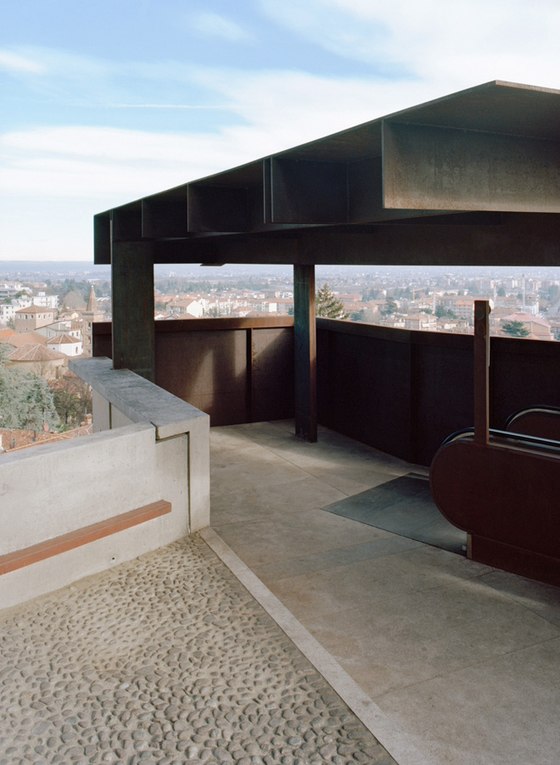
-Access by escalator: On the side of the hill facing Turin, an intricate pattern of visual relationships is woven by the cuts in the slope and the traces of the spaces embedded within the slope, and dynamically frames the specific scales present in the surroundings – a smaller version of the system of axes in Turin’s landscape, between Venaria Reale, Stupinigi, Superga and Rivoli. The ascent and descent take different paths: via ramps, terraces, stairs and escalators, and through galleries, courtyards and grottoes, a relaxed, rhythmic sequence of movement, deemed La Ronde, provides surprising views of the buildings in Rivoli’s historic centre and Turin’s landscape.
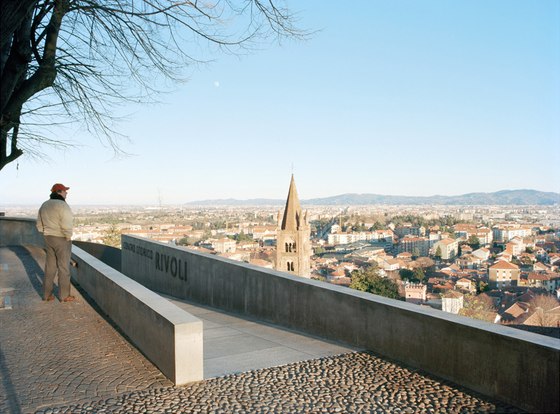
At the crest of this succession of paths, a loggia – the only element which projects from the slope – marks the access to the castle’s new forecourt, which is to remain open and be used as a venue for public events following the next building phase. The remains of a medieval row of buildings that were destroyed to make way for a castle terrace were unearthed during the construction work. They shall be provided shelter and integrated in the design to bear testimony to the strained relationship between the city and the castle. Extensions to the project are planned for the future: panelling and cantilevering roofs will be inserted in the walls without openings accompanying the historic centre’s streets intersecting with the steep slope and a square on the edge of the historic centre will provide the connection to a future metro-line station.
Comune di Rivoli (TO)
DI Johann Überlackner, Arqu. Luis Barbosa da Silva, Arch. Roland Fabiani, DI Paul Stöffler
Structural engineering: Gmeiner & Haferl, Ing.GesmbH, Wien
Studio Linea, Padova
Hydraulic engeneering: Studio Linea, Padova
Electric engineering: Studio Linea, Padova (Ing. Laura Romito)
Landscape engineering: Arch. Rosita Feltrin, Mestre
General contractor: S.I.E.G. S.p.A., Verdellino (BG)
Construction firm: Costante&C. Costruzioni s.r.l., Rivoli (TO)
Building locksmith: Ariotti s.r.l., Vercelli (VC)
Escalators, electric eng.: S.I.E.G. S.p.A., Verdellino (BG)